Our Blog
Check out our innovative pump solutions and industry insights to see what's new in the pumping industry. Stay up to date with the latest trends and news in the world of pumping technology by following our pumping technology blog.
- Home
- Blog
What is a Submersible Well Pump and How Does It Work?
A submersible well pump is a crucial component in modern water extraction systems, designed to efficiently move water from underground sources to the surface. These pumps are submerged beneath the water level, allowing them to operate in a compact and streamlined manner. The mechanics of a submersible well pump involve a motor that drives an impeller, which creates pressure to push water through the pump and into pipes for distribution. Understanding the intricacies of how these pumps work is essential for anyone involved in agricultural, residential, or commercial water supply management.
In essence, submersible well pumps offer a reliable and energy-efficient solution for accessing groundwater, especially in areas where surface water is scarce or of poor quality. Their design minimizes the need for complex piping, as they can be placed directly in the water source, making installation and maintenance more straightforward. By comprehensively exploring the functionality and operational principles of submersible well pumps, this article seeks to illuminate their significance in both residential and industrial applications, while also highlighting the best practices for their use and maintenance.
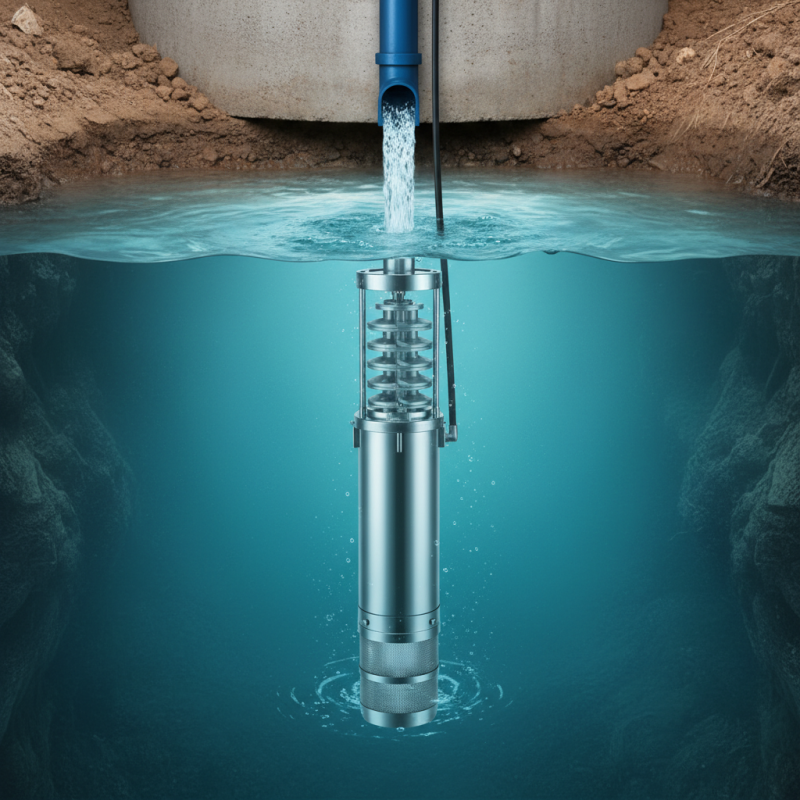

What is a Submersible Well Pump? Definition and Overview
A submersible well pump is a type of pump designed specifically for drawing water from deep underground sources such as wells. Unlike traditional pumps that are installed above the water level, submersible pumps operate underwater, which allows them to push water to the surface more efficiently due to the hydrostatic pressure of the water column. Typically used in residential, agricultural, and industrial applications, these pumps are essential for ensuring a reliable water supply, especially in areas where groundwater is the primary source.
According to industry reports, submersible pumps can operate at depths ranging from 25 to 300 feet, with some advanced models capable of reaching even deeper levels. The pump consists of a motor and a pump body encased in a hermetically sealed structure to protect the components from water and debris. This design not only enhances the pump’s efficiency but also reduces noise and energy consumption. The U.S. Department of Energy notes that submersible well pumps can achieve over 80% efficiency in properly configured settings, making them an energy-efficient choice for long-term water extraction. Their durable materials and corrosion-resistant coatings also contribute to a longevity that can exceed 15 years, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance.
Key Components of a Submersible Well Pump: A Technical Breakdown
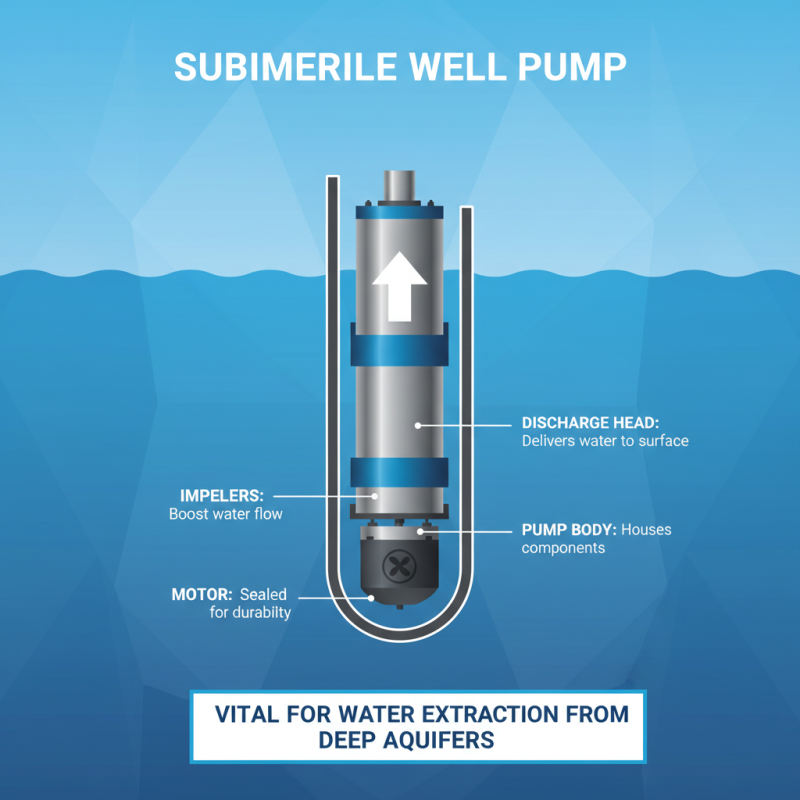
A submersible well pump is a vital component in water extraction systems, designed to operate underwater. Its primary function is to draw water from deep aquifers and deliver it to the surface. Key components that make up a submersible well pump include the motor, pump body, impellers, and discharge head. The motor, typically located at the bottom of the system, is hermetically sealed to prevent water ingress, ensuring durability and longevity even in challenging conditions. The impellers, designed to efficiently transfer energy from the motor to the water, are crucial for maintaining optimal flow rates.
In industry analyses, it has been reported that submersible pumps can achieve efficiencies of up to 90%, significantly reducing energy consumption compared to traditional pumps. According to the Hydraulic Institute, the capability of these pumps to operate at greater depths while maintaining high efficiency makes them a preferred choice for agricultural, municipal, and residential applications.
**Tips:** When selecting a submersible well pump, consider the depth of your water source and the volume of water needed. Proper sizing ensures optimal performance and longevity. Additionally, regular maintenance is essential; checking for wear and tear can significantly extend the life of the pump and reduce the risk of costly replacements.
How Submersible Well Pumps Operate: The Mechanisms Behind the Process
Submersible well pumps are critical components in water extraction systems, particularly where groundwater resources need to be accessed efficiently. These pumps operate by being fully submerged in the water source, typically a well, and are designed to push water to the surface rather than pull it. The functionality of submersible pumps relies on several key mechanisms. When powered, an electric motor at the pump's base drives an impeller, which rotates rapidly to create centrifugal force. This force propels water upward through a series of stages, each consisting of fixed and rotating blades that increase pressure and facilitate movement.
According to the National Ground Water Association, approximately 15 million households in the United States utilize well water, highlighting the significance of reliable pumping systems. The design of submersible pumps often includes multiple impellers stacked vertically, allowing for increased flow rates and depth capability. The submittal of these pumps below ground level ensures lower hydraulic losses compared to surface pumps, which can lose efficiency due to atmospheric pressure. Furthermore, a report by the Global Market Insights indicates that the submersible pump market is anticipated to surpass $20 billion by 2026, underscoring the growing reliance on these sophisticated mechanisms not only in residential settings but also in agricultural and industrial applications.
What is a Submersible Well Pump and How Does It Work?
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Pump Type | Submersible Pump |
| Recommended Depth | Up to 400 feet |
| Power Source | Electric Motor |
| Typical Flow Rate | 5 - 100 GPM |
| Material | Stainless Steel or Thermoplastic |
| Installation Location | Underwater in wells |
| Maintenance Requirements | Regular inspections, cleaning, and testing |
| Advantages | Efficient water lifting, space-saving, quieter operation |
| Common Use Cases | Residential water supply, irrigation, dewatering |
Common Applications of Submersible Well Pumps in Various Industries
Submersible well pumps play a crucial role in various industries by efficiently extracting water from underground sources. In agricultural settings, they are commonly employed for irrigation purposes. Farmers rely on these pumps to maintain consistent water supply to crops, ensuring healthy growth and optimizing yield. The ability to install submersible pumps deep within wells allows agriculture to thrive even in arid regions where surface water is scarce.
In municipal applications, submersible well pumps are integral to supplying potable water to communities. Water treatment facilities utilize these pumps to draw water from aquifers, filtering and distributing it for residential and industrial use. Additionally, submersible pumps are essential in environmental monitoring and dewatering projects. In construction, they help manage groundwater levels at excavation sites, preventing flooding and ensuring safety during building operations. Their versatility makes submersible well pumps a vital component across different sectors, promoting sustainable water management practices.
Submersible Well Pump Applications Across Industries
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Strategies for Submersible Well Pumps
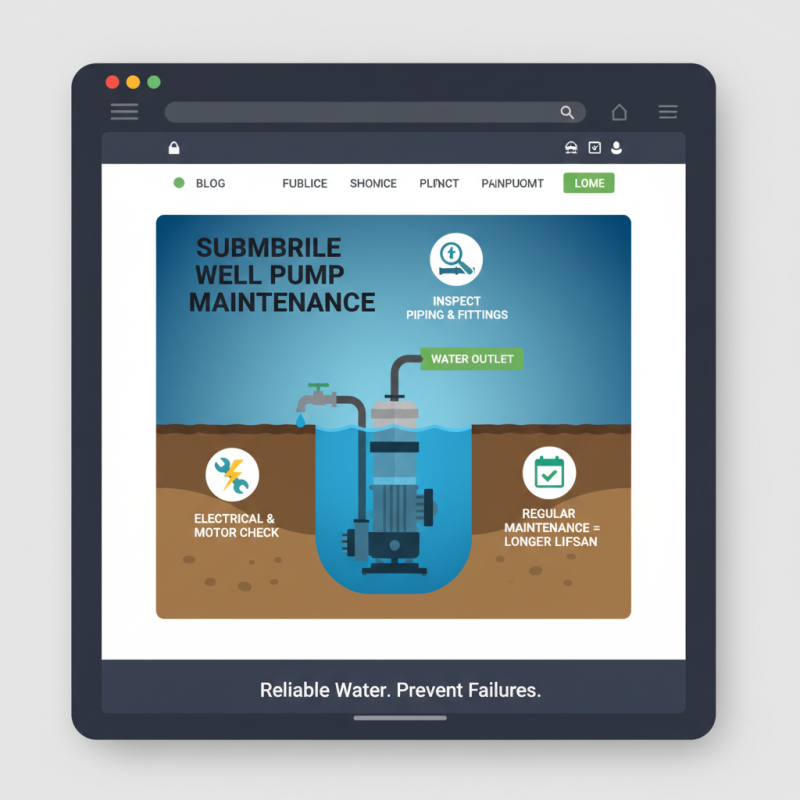
Submersible well pumps are essential for extracting water from deep underground sources, operating underwater to ensure efficiency and reliability. Proper maintenance is crucial to prolonging the lifespan of these pumps. Regular checks on electrical connections and motor functionality help prevent unexpected failures. Additionally, it is advisable to inspect the discharge piping and fittings for any leaks or corrosion, as these issues can significantly impact performance.
When troubleshooting a submersible well pump, it is important to evaluate the system methodically. Start by checking the power supply; ensure that the circuit breaker is functioning and the power is reaching the pump. If the pump fails to operate, it might be a sign of a faulty motor or impeller blockage. In such cases, removing the pump for a thorough inspection can identify issues like debris accumulation. Regularly monitoring the flow rate and water quality can also help in early detection of problems, allowing for timely interventions before major repairs are necessary.
Related Posts
-

Unlocking Efficiency: The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Motor Pump for Your Needs
-

Maximizing Efficiency: How Submersible Pumps Revolutionize Water Management in Agriculture
-

2025 Top 10 Domestic Water Pumps: Unmatched Efficiency and Performance You Need!
-

2025 Top 10 Deep Well Water Pumps: Ultimate Guide for Efficient Water Supply
-

2025 Guide: How to Choose the Best Small Submersible Pump for Your Needs
-

What is a Small Water Pump? Types, Uses, and Buying Guide Explained

